Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized industries, with significant advancements in large language models and generative AI. While these technologies often overlap in conversation, they serve distinct purposes and bring unique advantages to the table. This article delves deep into their definitions, functionalities, differences, use cases, and how to choose the right technology for your needs.
What Are Large Language Models?
1. Definition and Core Functionalities
Large language models (LLMs) are AI systems trained to understand, process, and generate human-like text. They are built using deep learning architectures, particularly transformer-based models, to analyze and generate text based on input data.
2. Examples of Large Language Models
- GPT-4: A state-of-the-art model by OpenAI known for generating coherent and contextually relevant text.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Developed by Google, used for understanding context in search queries.
- T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer): A versatile model capable of handling various NLP tasks.
3. Primary Applications
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Text summarization, sentiment analysis, and question-answering.
- Content Generation: Articles, reports, and creative writing.
- Language Translation: Accurate and context-aware translations.
- Customer Support: Chatbots and automated assistance tools.
4. Strengths
- High accuracy in understanding context.
- Versatility in solving diverse language-based tasks.
- Ability to improve user experience in applications like search engines and voice assistants.
What Is Generative AI?
1. Definition and Scope
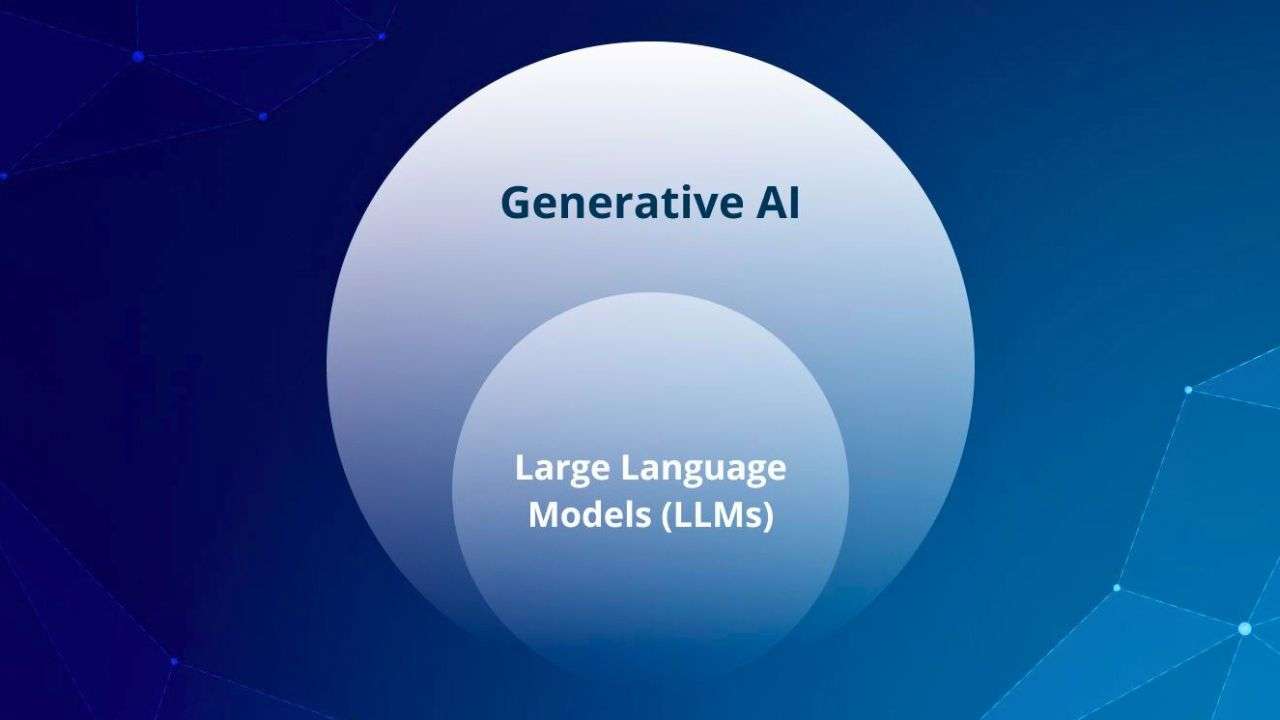
Generative AI refers to algorithms capable of creating new, original content such as text, images, music, or videos. Unlike large language models that focus on text, generative AI can work across multiple modalities.
2. Examples of Generative AI Tools
- DALL·E: Creates realistic images from textual descriptions.
- Stable Diffusion: Generates high-quality visuals and artwork.
- ChatGPT: Combines LLM capabilities with conversational AI for text-based interactions.
3. Applications Beyond Text
- Visual Arts: AI-generated paintings, graphic designs, and illustrations.
- Music Composition: Original compositions for media and entertainment.
- Video Creation: Automated video editing and scene generation.
4. Strengths
- Versatile creative outputs across various media.
- Enhanced capabilities in entertainment, marketing, and design.
- Ability to innovate in fields like gaming and virtual reality.
Key Differences Between Large Language Models and Generative AI
1. Text-Focused vs. Multimodal Outputs
- Large Language Models: Primarily excel in text-related tasks, such as language understanding and generation.
- Generative AI: Capable of producing content in multiple formats, including text, images, audio, and video.
2. Specialized vs. Generalized Use Cases
- LLMs are specialized in handling structured language tasks like summarization and translation.
- Generative AI extends its functionality to creative industries, producing synthetic media for various applications.
3. Architectural Differences
- LLMs are transformer-based models trained on text datasets.
- Generative AI combines neural networks and generative adversarial networks (GANs) for multimodal outputs.
4. Performance Metrics
- LLMs are evaluated based on linguistic coherence and contextual accuracy.
- Generative AI focuses on creative originality and realism in outputs.
Use Cases of Large Language Models
1. Chatbots and Customer Service Automation
- Creating conversational agents for businesses.
- Providing 24/7 support with human-like interactions.
2. Document Summarization and Legal Tech
- Extracting key points from lengthy documents.
- Assisting legal professionals in case analysis and contract drafting.
3. Language Translation and Content Moderation
- Translating texts across multiple languages while retaining context.
- Detecting and moderating harmful or inappropriate content.
4. SEO-Focused Content Generation
- Generating blog posts, articles, and meta descriptions.
- Ensuring content is keyword-rich and ranks well in search engines.
Use Cases of Generative AI
1. Creative Content Generation
- Producing unique visuals for marketing campaigns.
- Creating storyboards and scripts for media projects.
2. Gaming and Virtual Reality Experiences
- Designing immersive game worlds with AI-generated assets.
- Enhancing user experiences through interactive narratives.
3. Synthetic Media for Marketing and Advertising
- Generating customized ads tailored to specific audiences.
- Creating virtual influencers for brand promotions.
4. Prototyping for Design and Engineering
- Rapidly developing product prototypes using 3D models.
- Simulating architectural designs and engineering solutions.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technology
1. Advantages of Large Language Models
- High accuracy in processing complex text.
- Reliable performance in NLP-driven applications.
- Streamlined workflows for industries like journalism and customer service.
2. Advantages of Generative AI
- Expands creative possibilities in art and entertainment.
- Speeds up production cycles for content creation.
- Breaks barriers in innovation with synthetic data generation.
3. Limitations
- LLMs: Limited by their inability to process non-textual data; require extensive computational resources.
- Generative AI: Faces ethical concerns regarding copyright, misinformation, and deepfake creation.
Choosing Between Large Language Models and Generative AI
1. Factors to Consider
- Objective: Are you working on text-focused tasks or creative projects?
- Resources: Assess the computational power and data availability for training models.
- Scalability: Determine the scalability of the chosen solution for long-term needs.
2. When to Use Large Language Models
- Applications requiring natural language understanding and text generation.
- Scenarios like content creation, language translation, and customer support.
3. When to Use Generative AI
- Creative industries demanding high-quality visuals, audio, or video.
- Innovative applications in gaming, marketing, and prototyping.
Conclusion
Large language models and generative AI are transformative technologies that cater to different needs. While LLMs specialize in understanding and generating text, generative AI transcends into creative domains, producing stunning visuals and immersive content. The choice between these technologies hinges on your project’s goals and requirements. Whether you’re crafting SEO-friendly articles or designing AI-generated art, the right tool can unlock unprecedented possibilities. Ready to integrate AI into your workflow? Explore the best tools today.
Read Also:
Top 10 High-Paying AI Skills to Learn in 2025
SQL vs NoSQL Cloud Database: Which One is Right for Your Business in 2025?